D-Link Firmware
D-Link Firmware:
DIR-2640_REVA_FIRMWARE_1.11B02
After extracting the firmware using binwalk, drag prog.cgi into IDA for analysis:
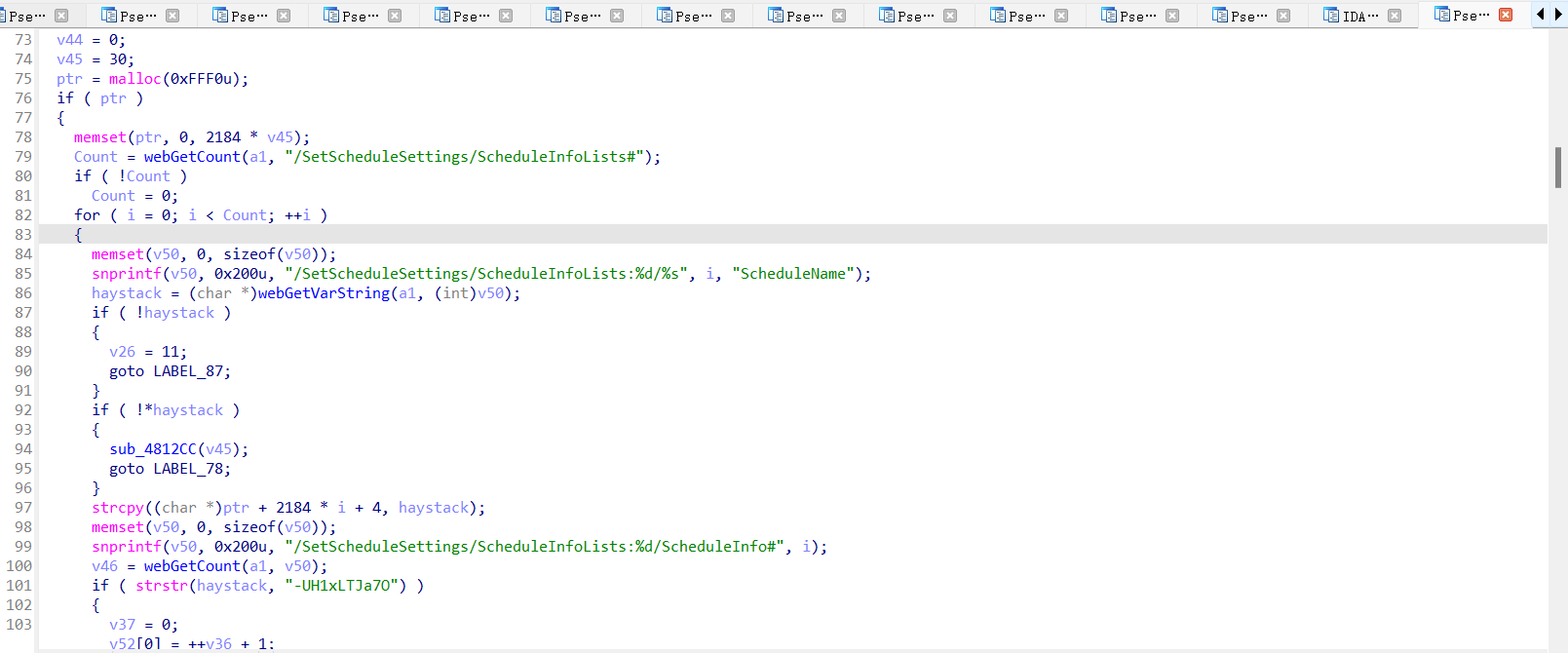
In the sub_481FC8 function, we can see a variable count controlling the number of iterations of a for loop. Within the loop, the strcpy function is used to copy haystack into ptr. However, since count is not validated, if count is sufficiently large, it can cause a heap overflow.
Checksec Analysis:
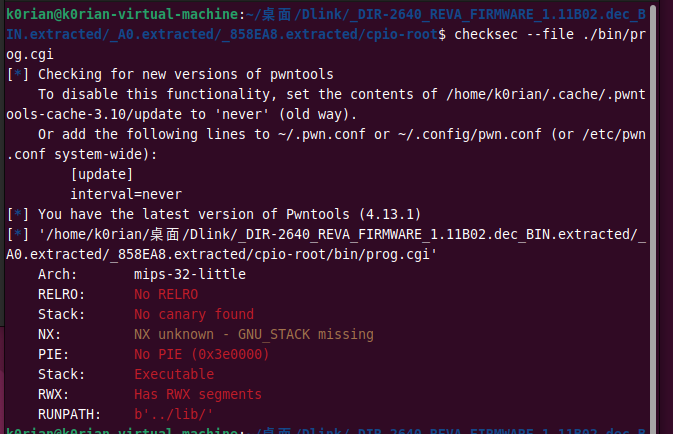
It turns out that no protections are enabled. First, let’s test it under QEMU in user mode. Run prog.cgi: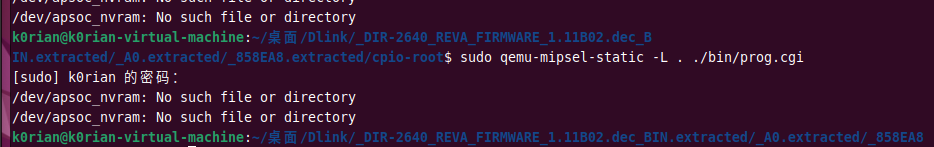
It seems some devices are not mounted, so let’s first start a chroot container and run rcS:
1 | chroot . ./qemu-mipsel-static ./bin/ash |
Although there are some issues, some disks are successfully mounted. Now let’s try running prog.cgi again:
It throws an error. After debugging, we found that the program exits at the sub_42D2DC function. This function is a registry function that triggers an ioctl error when calling the trace function. Therefore, we patched it, successfully entering the main loop:
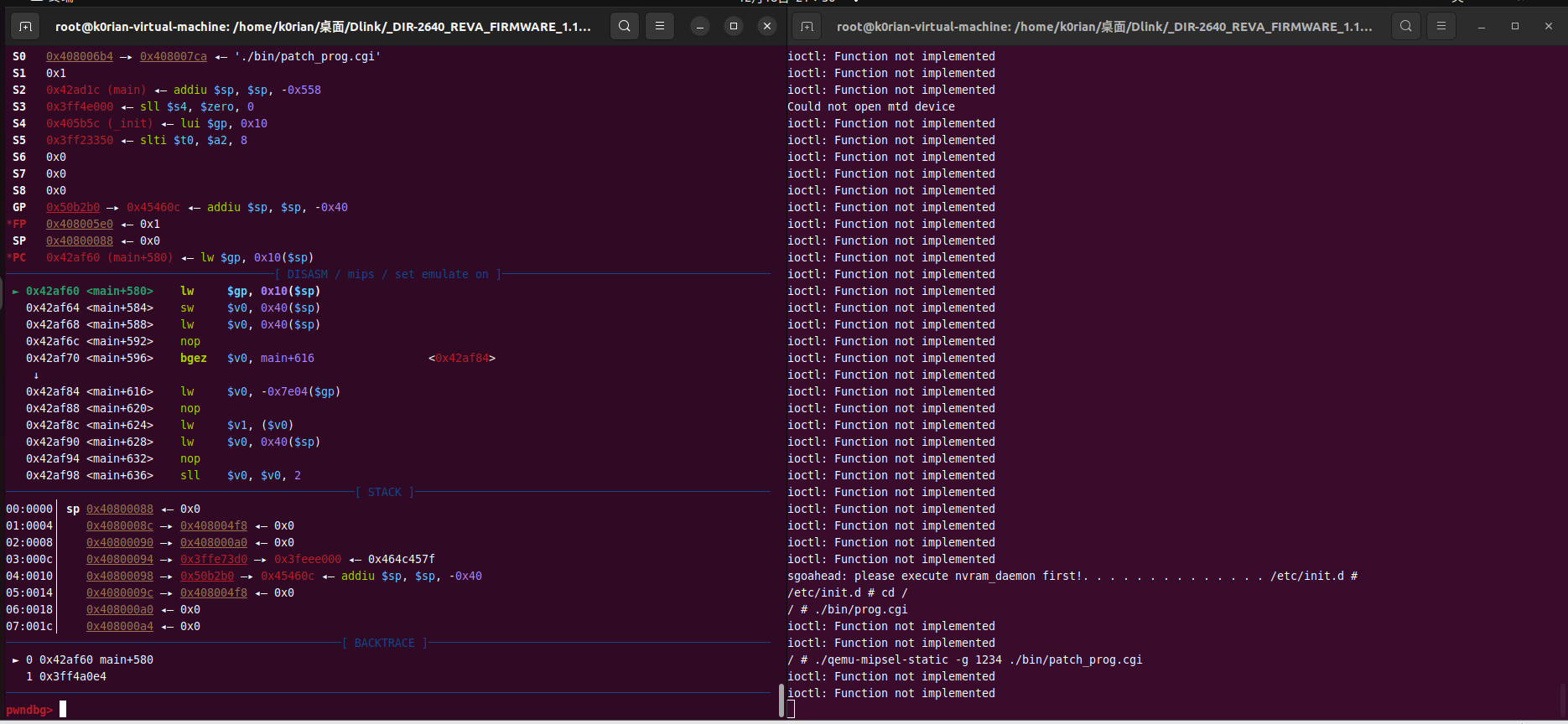
Later, we discovered that this program does not communicate over the network but instead uses the getenv function to interact with the web application via environment variables. Despite various attempts, the author could not successfully launch the entire web application, so another approach was needed.
How to Make the Program Crash:
The vulnerable code is as follows:
1 | ptr = malloc(0xFFF0u); |
To trigger the loop and reach strcpy, two conditions must be satisfied:
webGetVarStringmust return a valid value.*haystackmust not be empty.
Once these two conditions are met, the strcpy function will be called within the loop, copying up to 0x888 bytes from haystack into ptr. To keep the loop running, observe the following part of the code:
1 | memset(v50, 0, sizeof(v50)); |
To simplify the model, set v46 to 0 so the if branch is skipped. After entering else, the program will proceed to the next iteration of the loop, achieving our objective.
Debugging Method:
Copy qemu-mipsel-static to the root directory of the firmware. Start the chroot container and run the following commands:
1 | cp /usr/bin/qemu-mipsel-static . |
In another terminal, start gdb-multiarch:
1 | gdb-multiarch |
Hooking into the sub_481FC8 Function:
Write a main_hook.so library to hook into the sub_481FC8 function using libc_start_main. Provide an arbitrary input, setting count to 64. Below is seeds.bin:
1 | AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA |
The I/O hook function is as follows: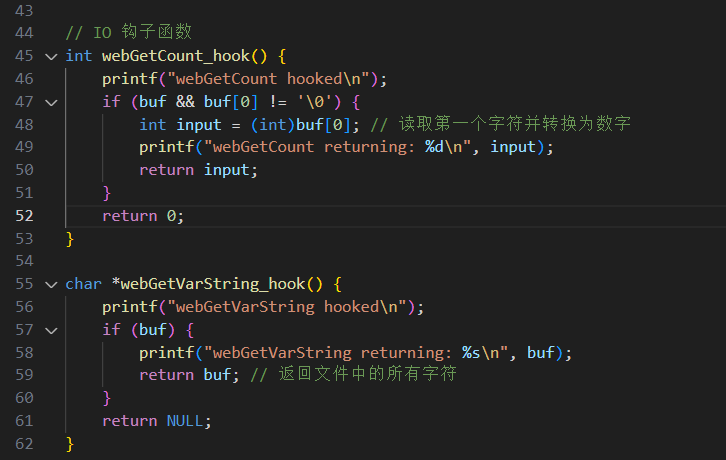
With 64 uppercase ‘A’s, set LD_PRELOAD to main_hook.so and run the following command:
1 | chroot . ./qemu-mipsel-static -L . -E LD_PRELOAD=/lib/libdl.so.0:./stack_hook.so -g 1234 ./bin/prog-cgi seeds.bin > log.txt |
Debug further, and notice a segmentation fault: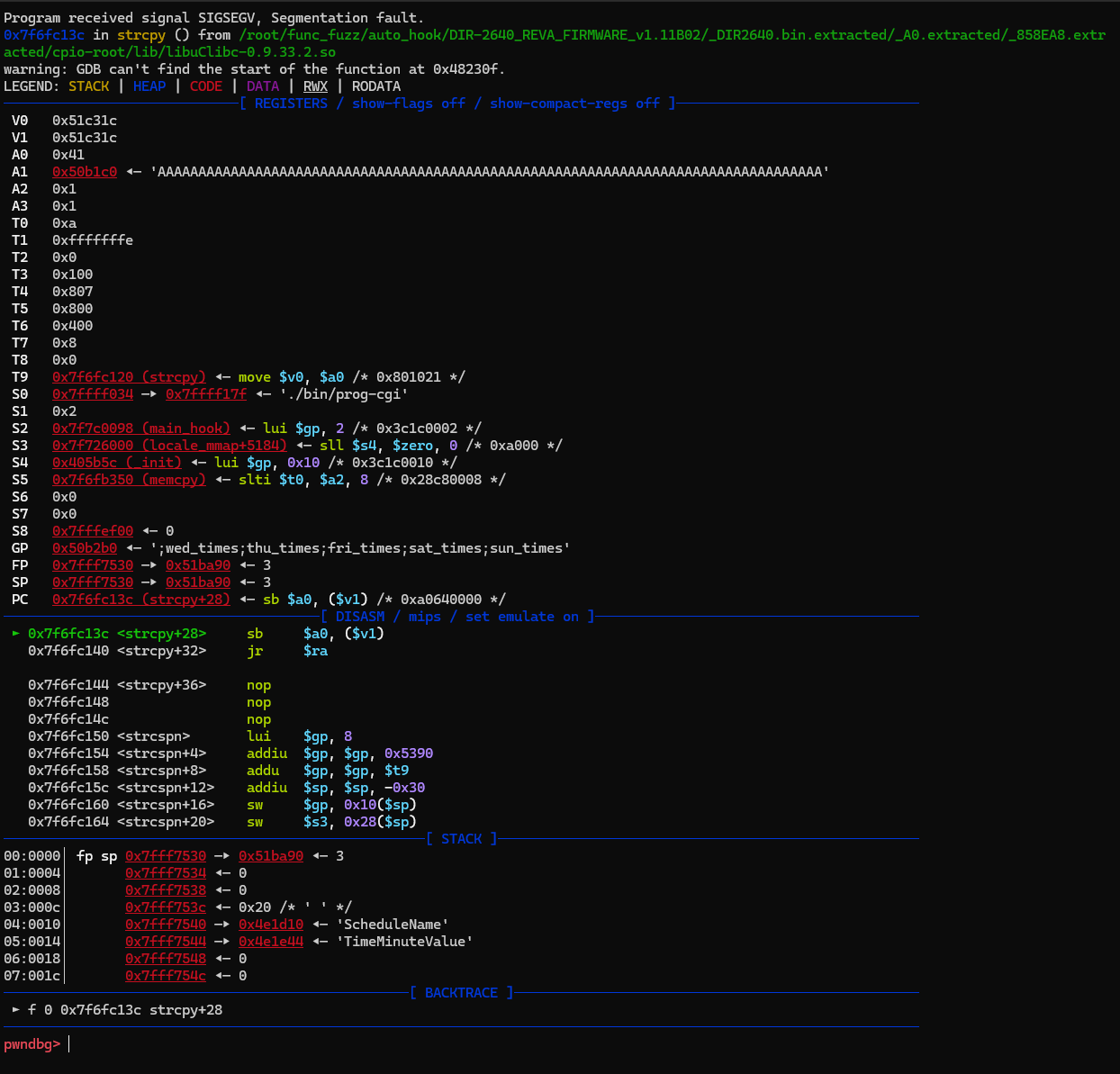
Upon inspection, it turns out the haystack string overwrote the ptr below it, causing an error when dereferencing ptr. In short, this is a buffer overflow that allows arbitrary write primitives.
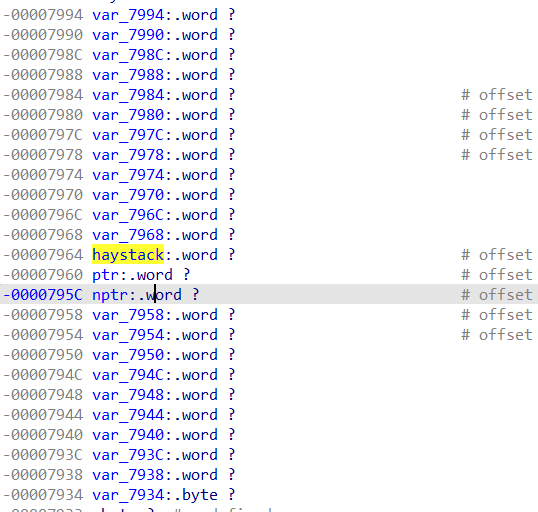
The stack structure is as follows: